Crusher for vehicle and construction triplex glass
Using
The crushing line is specifically designed to efficiently crush automotive and construction glass manufactured using triplex technology, with a maximum thickness of 10 mm.
Device and principles of functioning
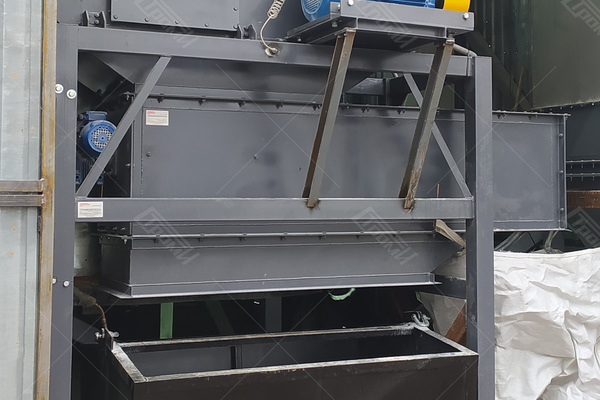
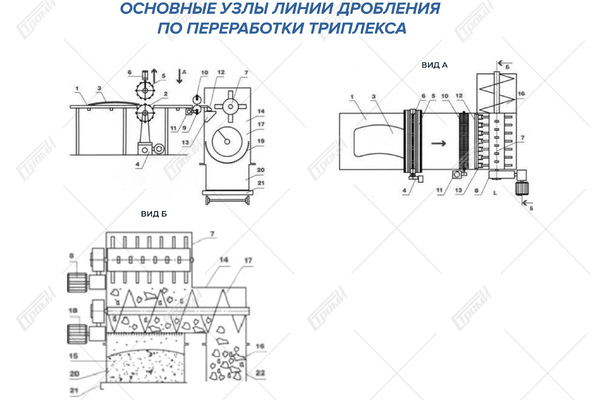
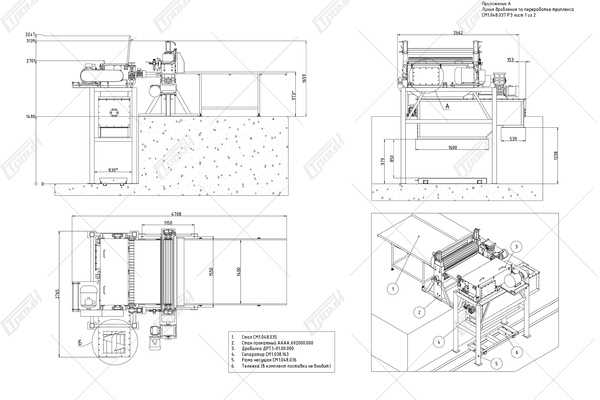
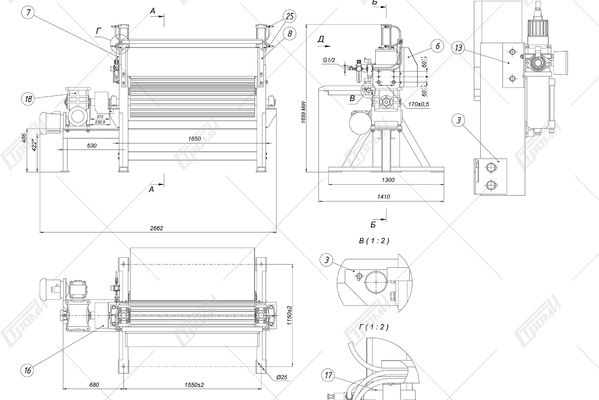
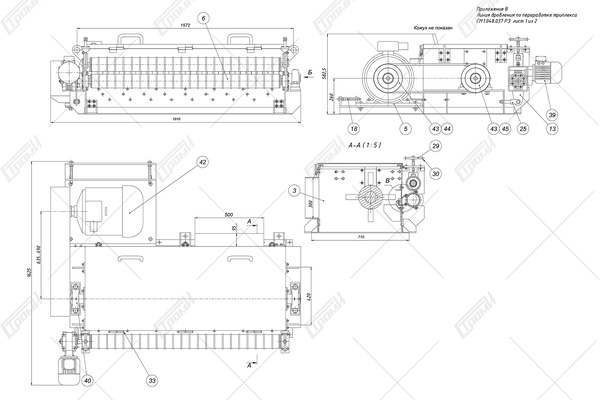
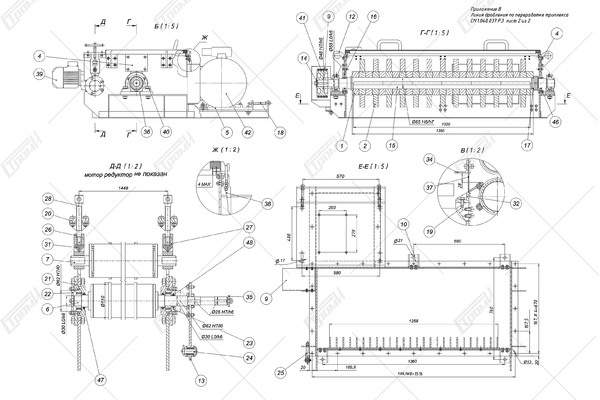
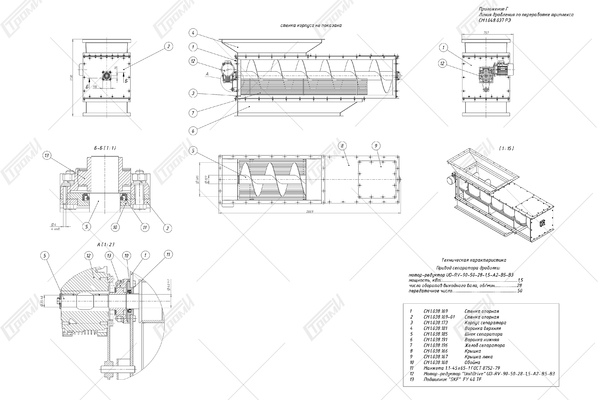
This crushing line comprises the following components (refer to the photo below): a receiving table 1, a conveying mechanism 2, an electric drive system for the conveying mechanism 4, a movable ribbed shaft 5 with a pneumatic vertical movement drive 6, a rotary crusher 7 with an electric drive 8, a glass feeding assembly for the rotary crusher. This assembly includes a driven roller shaft 9 with an electric drive 11 and a non-driven roller shaft 10, a crushing bar 12, and knives 13 for cutting the film. Additionally, there is a separator 14 consisting of a helical feeder 17 with an electric drive 18 and a perforated bottom 19. The crushed glass is collected in container 20, which is mounted on a transport carriage 21, and the separated film is stored in container 22. Please note that containers 20, 22 and the transport carriage 21 are not included in the package.
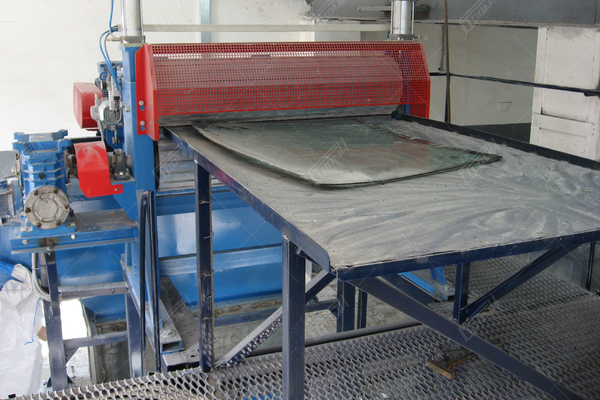
In the initial state, the triplex glass 3 is placed on the receiving table 1, which is equipped with the transportation mechanism 2 with the electric drive 4 turned off. If the recycled glass has a flat shape, the adjustable clearance between the permanently installed ribbed shaft of the mechanism 2 and the vertically movable ribbed shaft 5 is a few millimeters and varies depending on the thickness of the recycled glass, ranging from 5 to 10 mm. In the case of curved glass, before crushing, the finned roller 5 is raised by approximately 10 to 15 cm using the pneumatic drive 6, allowing the glass with a curved surface to enter the gap between the finned rollers.
The operation of the unit begins when the operator activates the electric drives of all mechanisms and initiates the glass feeding process into the gap between the ribbed rollers 2 and 5. When processing flat laminated glass, the glass is gripped by rollers 2 and 5 and transported to the glass feeder for the rotary crusher 7, which is controlled by the electric drive 8. During transportation, the ribbed surface of the rollers 2 and 5 causes the glass to crack, transforming it into a semi-rigid structure composed of glass fragments of various shapes, bonded together by an adhesive film.
In the case of curved triplex glass, it is also fed into the gap between the ribbed rollers 2 and 5, but initially, the roller 5 is raised by 10 to 15 cm using the pneumatic drive 6. The glass is pre-broken without separating the glass fragments from the film. As the curved glass enters the gap between the ribbed rollers, the pneumatic actuator 6, triggered by the control system, lowers the ribbed roller 5 onto the glass 3 and crushes it, giving the glass a flat shape.
During the process of preliminary glass breaking and its transportation to the rotor crusher, the pneumatic cylinders of the pneumatic drive 6 serve not only to squeeze the glass between the ribbed rollers but also act as pneumatic shock absorbers, allowing adaptive interaction between the ribbed surfaces of rollers 2 and 5 and the glass surface.
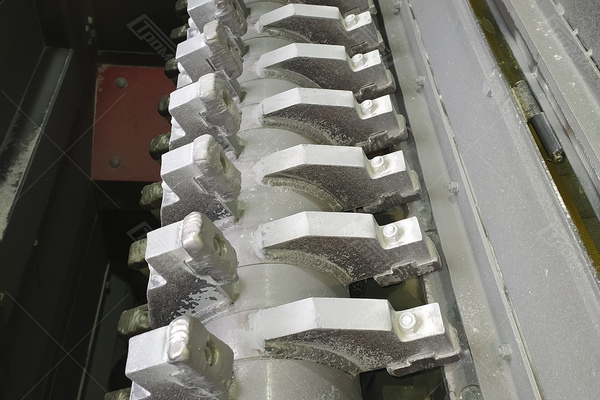
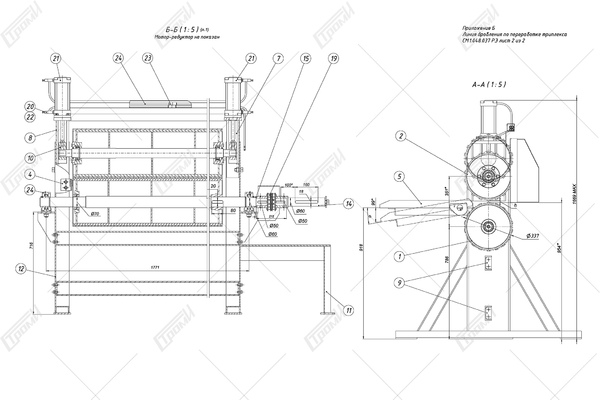
After the preliminary breaking, as the glass 3 is being transported, it enters the gap between the spring-loaded roller shafts 9 and 10, whose rotation is driven by the electric drive 11. These shafts firmly grip the glass and convey it towards the area of the crushing bar 12. The direct crushing and effective separation of the glass from the film occur through the impact of the rotating crusher rollers on the glass edges, within the gaps between the rollers and the crushing bar. The spring-loaded rollers 9 and 10 securely hold the glass, preventing it from abruptly catching the crushing bead, while stabilizing the glass supply into the crushing zone.
After the glass is crushed and separated from the film, the film is torn into separate pieces by the rotating rollers and knives positioned beneath the crushing bar. During the film breaking process, any remaining fragments of unseparated glass are further separated, and the glass itself is directed into the separator 14. In the separator, clean glass slugs 15 with a size not exceeding 10-15 mm are segregated from the film fragments 16, which are larger in size than the separated glass particles. The glass fiber particles 15 fall through the perforated bottom 19 and accumulate in the container 20 mounted on the transport cart 21, while the film fragments are transported by the screw feeder 17 as it rotates and discharged into the container 22. As the containers 20 and 22 become filled with glass and film, they can be rolled aside for unloading or replaced with new ones.
technical specifications
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Maximum thickness of the processed triplex, mm | 10 |
| Highest output, t/h | 0,8...1 |
| Triplex feeding speed, m/s | 0,157 |
| Size of the fraction of the resulting glass scrap, mm | 10...15 |
| Efficiency of glass separation from film, % | 75...85 |
| Probability of film penetration into the glass, % | 3...5 |
| Number of crusher hammers, pieces | 27 |
| Operating pressure of the pneumatic system, MPa | 0,5...0,6 |
| Requirement for compressed air cleaning | Class 7 GOST 17433-80 |
| Rolling mill drive speed, rpm | 9,375 |
| Crusher feed drive speed, rpm | 70 |
| Crusher rotor drive speed, rpm | 1500 |
| Separator drive speed, rpm | 28 |
| Total power consumption, kW | 27,6 |
| Power consumption of rolling mill drive, kW | 3,0 |
| Power consumption of crusher feed drive, kW | 1,1 |
| Power consumption of crusher rotor drive, kW | 22,0 |
| Power consumption of separator screw drive, kW | 1,5 |
| Degree of protection of electric motors | IP54 |
| AC supply voltage, V | 380 ± 30 |
| Total weight, kg | 2930 |
| Table weight, kg | 95 |
| Weight of the rolling mill, kg | 1050 |
| Crusher weight, kg | 952 |
| Separator weight, kg | 576 |
| Weight of the supporting frame, kg | 257 |